Introduction
Heart valve replacement surgery has been a lifesaving procedure for thousands of patients over the years. Traditional heart valve replacement surgery involves an open-heart procedure, which can be risky and require a long recovery time. However, the development of the Sapien artificial heart valve has revolutionized heart valve replacement surgery. The Sapien valve is inserted into the heart through a small incision, making the procedure much less invasive and reducing recovery time. In October 2012, the use of the Sapien valve was expanded to include patients who are not candidates for traditional heart valve surgery. In this article, we will explore the features of the Sapien valve and the implications of its expanded use.
The Sapien Valve
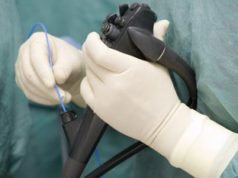
The Sapien valve is a bioprosthetic valve that is made from animal tissue and mounted on a stent frame. The valve is designed to be inserted into the heart through a small incision in the leg or chest, using a catheter. Once in place, the valve expands to fit the patient’s natural valve, effectively replacing the damaged or diseased valve.
The Sapien valve has been used successfully in patients with aortic stenosis, a condition where the heart’s aortic valve becomes narrow and obstructs blood flow. The valve has been shown to reduce symptoms and improve survival rates in patients with this condition compared to medical management alone.
Expanded Use
In October 2012, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the expanded use of the Sapien valve for patients who are not candidates for traditional heart valve surgery. This includes patients who are considered high-risk for open-heart surgery due to factors such as their age, frailty, or other medical conditions.
The expanded use of the Sapien valve opens up new treatment options for these patients, who may have previously been deemed too high-risk for surgery. With the use of the Sapien valve, these patients can undergo heart valve replacement without the high risks associated with open-heart surgery.
Implications for Patients and Healthcare Providers
The expanded use of the Sapien valve has important implications for patients and healthcare providers. Patients who are not candidates for traditional heart valve surgery can now receive life-saving treatment with a less invasive procedure. This can improve their quality of life and potentially extend their lifespan.
For healthcare providers, the expanded use of the Sapien valve offers a new treatment option for high-risk patients. The minimally invasive procedure and reduced recovery time also mean that patients can be treated more efficiently, which can lead to cost savings for the healthcare system as a whole.
Conclusion
The expanded use of the Sapien artificial heart valve offers new treatment options for patients who are not candidates for traditional heart valve surgery. The minimally invasive procedure and reduced recovery time can improve patient outcomes and potentially extend their lifespan. For healthcare providers, the expanded use of the Sapien valve offers a new treatment option for high-risk patients and can lead to cost savings. As the use of the Sapien valve continues to expand, it is important to carefully evaluate patient suitability and ensure that best practices are followed for the safe and effective use of this innovative technology.
On October 19, 2012, the Food and Drug Administration approved the expanded use of the Sapien Transcatheter Heart Valve (THV). Patients with aortic valve stenosis who can receive surgery but appear at risk of serious complications during surgery are now approved for the heart valve.
The Sapien THV was first approved in 2011 for patients who could not undergo surgery for aortic valve stenosis. The condition occurs when calcium deposits occur on the aortic valve and cause it to narrow. The heart will eventually work harder to push blood through the reduced opening, and aortic valve stenosis can eventually lead to fainting, chest pain, heart failure, arrhythmias, or even cardiac arrest.
The Sapien THV does not require a surgeon to open the chest or heart. Instead, the THV is compressed into a small tube referred to as a delivery catheter. The delivery catheter and the THV are then placed in the femoral artery in the leg and threaded to the bad valve. Lastly, the THV is released from the delivery catheter and then increased to normal size with a balloon. The inserted THV begins working right away.
The use of the Sapien THV was expanded after a clinical study compared results between 348 patients who received the THV through the delivery catheter and 351 patients who received a valve replacement during open-heart surgery. The groups experienced similar death rates during the first month, first year, and first two years. THV recipients are at an increased risk of artery dissection or perforation, and the same patients are at risk of stroke during the first month after the procedure.
Christy Foreman, the director at the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, stated, “Any procedure to replace the aortic valve carries the risk for serious complications, but for some patients with coexisting conditions or diseases that risk may be especially high. The THV serves as an alternative for some very high-risk patients.”
Source: U.S. Food and Drug Administration